Types of water pumps
We must consider two basic types of pumps: the surface pumps and submersible pumps. The surface pumps are limited in suction height to a maximum of 7 m therefore submersible pumps are generally more efficient, lying dipped into the well bore or tank where they do water extraction. In the case of borehole typically it takes more than a very deep pit in which the hole diameter is also an important parameter.
 Submersible water pump with float for well protection Submersible water pump with float for well protection |
 Surface water pump (centrifugal) Surface water pump (centrifugal) |
 Submersible pump hole Submersible pump hole |
Water pumps, what information is needed?
In a typical case of water supply to a dwelling or irrigation system, the choice of pump depends primarily on the pressure (directly related to the gauge height) and the flow rate of water required.
If you want to know what the water pump suitable for your case, contact us by phone or email with the following information:
- Depth of well / bore;
- Distance from the well to the worst point;
- Drop the well to the worst point;
- If there is already piping which diameter;
- In the case of a dwelling / building supply, how many taps / water emitters are intended to feed simultaneously;
- In the case of watering, many sprinklers are intended to feed simultaneously, and what type of nozzle installed;
- If the target system is automatic or manually starts the pump whenever you want water.
The gauge height is essentially dependent on all heights and distances that the pump has to overcome, including:
- Depth of well / bore / spot of the liquid;
- Drop to the worst point;
- Distance to the worst point.
The flow is mainly dependent on:
- Debt required, either from a building supply, irrigation, drainage, etc .;
- The diameter of the pipe (there is a limit to the amount of water that can pass a certain openness with low losses).
Flow of Water Pump
Is determined by adding the capacity of all issuers of water: faucets, showers, sprinklers, sprayers, irrigation drop-by-drop systems, etc.
. equipment The following table shows usually found in a residential installation
| Equipment | Flow (L / s) | flow rate (L / min) Flow rate (L / h) | tube diameter (mm) Pressure (bar) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sanita | 0.15 | 9 | 540 | 22 | 2.5 |
| Shower | 0.12 | 7 | 420 | 22 | 2.5 |
| lavatory faucet | 0.15 | 9 | 540 | 22 | 2.5 |
| Dishwasher / clothing | 0.25 | 15 | 900 | 22 | 2.5 |
| Washer | 0.25 | 15 | 900 | 22 | 2.5 |
| garden hose | 0.33 | 20 | 1200 | 22 | 2.5 |
| hose irrigation | 0.60 | 36 | 2160 | 22 | 2.5 |
For example, a shower, a dishwasher and a sink operating simultaneously requires a flow rate 0.52 L / s, 31 L / min, 1860 L / h. However, it should be noted that only a garden hose requires a flow rate of 36 L / min.
Typical household flow rates:
| Application | L / min | L / h |
|---|---|---|
| small house | 20-30 | 1200-1800 |
| average house | 30-50 | 1800-3500 |
| big house | 50-90 | 3500-5400 |
This data is also dependent on how many people live in a household, ie how many taps are opened simultaneously.

Hydraulic flow advised facilities
Pressure / Height Gauge Water Pump
The operating pressure of the pump system is related to the gauge height and essentially depends on the vertical height that the pump must overcome and the desired pressure at the farthest point. You must also calculate in gauge height, all the losses along the pipe (caused by filters, valves, uneven terrain, length and size of tubing).
deemed to be for domestic applications a pressure of 2.5 bar (which for the calculation corresponds to 25 m gauge height) is perfectly suitable for most situations, like taps, showers, washing machines and dishwashers.
After calculated the gauge height and flow, consults hydraulic curves (curves of the pumps) to choose a pump that has the desired performance.
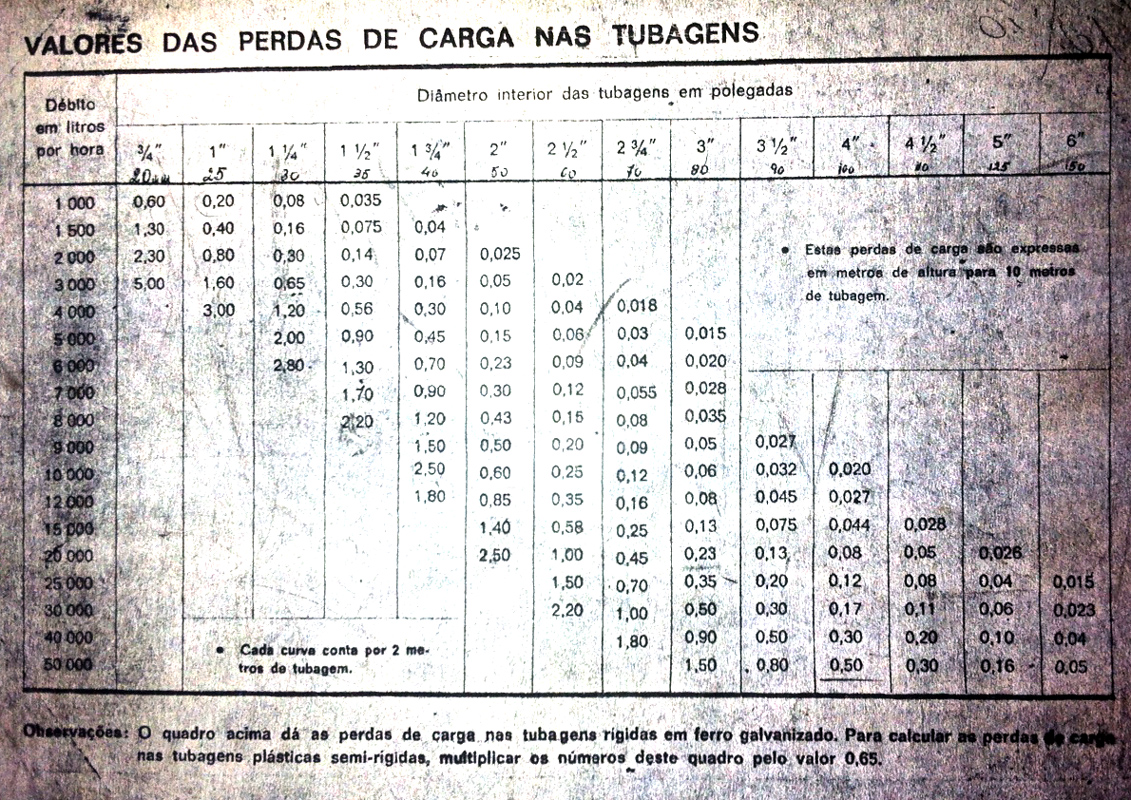
Diameter Tubing, Flow and Load Losses
Is the measure by which the tubes are known in the trade and industry in the same way in the next column is in inches in the first column of the following table. Next, described is the actual inner diameter of the pipe in mm. Also include the maximum recommended flow rate to a speed of 2 m / s and the corresponding loss of load per meter of pipe at head height.
| Measure | in inches | actual inside diameter (mm) | Section (mm ²) | max flow ( L / s) Max Flow (L / h) Pressure loss per m pipe (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 3/8 " | 8.8 | 61 | 0.1 | 360 | 0.6 |
| 15 mm | 1/2 " | 13.6 | 145 | 0.3 | 1080 | 0.3 |
| 22 mm 3/4 " | 20.2 | 320 | 0.6 | 2160 | 0.25 | |
| 28 mm | 1 "26.2 | 539 | 1.1 | 3960 | 0.2 | |
| 35 mm | 11/4 " | 32.6 | 835 | 1.7 | 6120 | 0.15 |
| 42 mm | 11/2 " | 39.6 | 1232 | 2.5 | 9000 | 0.1 |
| 54 mm | 2 " | 51.6 | 2091 | 4.2 | 15120 | 0.07 |
Through the values of pressure loss in pipes, which can quickly check is dependent on the flow tube diameter. For example, for a flow rate of 4000 L / h is recommended to use a tube 1 “1/2 (at least 1” quarter) or otherwise load losses in the piping will be very significant.
Pump Curve
After the known head height and the last step for selecting required flow of the pump is to consult the pump curve. The pump will have to work ideally in the middle of the curve in the most unfavorable point.
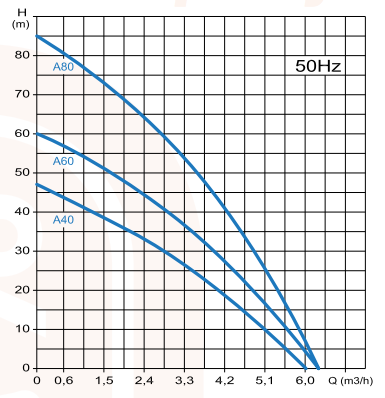
Curves Hidraulicas A40 A60 A80 Aqualiju
For example, for a flow rate of 3300 L / h and a delivery head of 35 m, the model is ideal pump A60 (middle curve) and have an outlet pressure in the most unfavorable point of 3.5 bar.
We can also see the problem from another perspective. Considering these hydraulic A80 model curves the half of the curve 45 mo which corresponds to a rate of about 4000 l / h which is the ideal working condition for this pump. These working conditions the pump will have an output pressure in the most unfavorable point of 4.5 bar.
Documentation
Technical Appendix selection of water pumps brand ESPA (Spanish)